Introduction
The industrial landscape has witnessed a dramatic transformation with the advent of robotics and automation. As these technologies evolve, they redefine manufacturing processes, increasing efficiency, precision, and flexibility. This article explores the latest advancements in robotics, the integration of automation in manufacturing, and the benefits and challenges associated with adopting these technologies.
The Evolution of Robotics in Manufacturing
Historical Context
The journey of robotics in manufacturing began in the early 1960s with the introduction of Unimate, the first industrial robot. This marked the beginning of a new era, where robots started performing repetitive and hazardous tasks, ensuring higher safety and productivity.
Technological Advancements
Today’s robots are far more advanced, equipped with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and sophisticated sensors. These innovations enable robots to perform complex tasks with remarkable precision. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans, enhancing the synergy between human intelligence and robotic efficiency.
Integration of Automation in Manufacturing
Automation Levels
Manufacturing automation can be categorized into three levels:
- Fixed Automation: Used for high-volume production, involving specialized equipment for specific tasks, such as assembly lines.
- Programmable Automation: Suitable for batch production, allowing reprogramming of machines for different tasks.
- Flexible Automation: Ideal for low to medium-volume production, offering the ability to switch between tasks with minimal reconfiguration.
Technologies drive automation:
Several technologies drive automation in manufacturing:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Connects machines and systems, enabling real-time data exchange and analytics.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhance decision-making, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
- Advanced Robotics: Perform tasks with high precision, adaptability, and efficiency.
- Cloud Computing: Provides scalable computing resources and storage, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
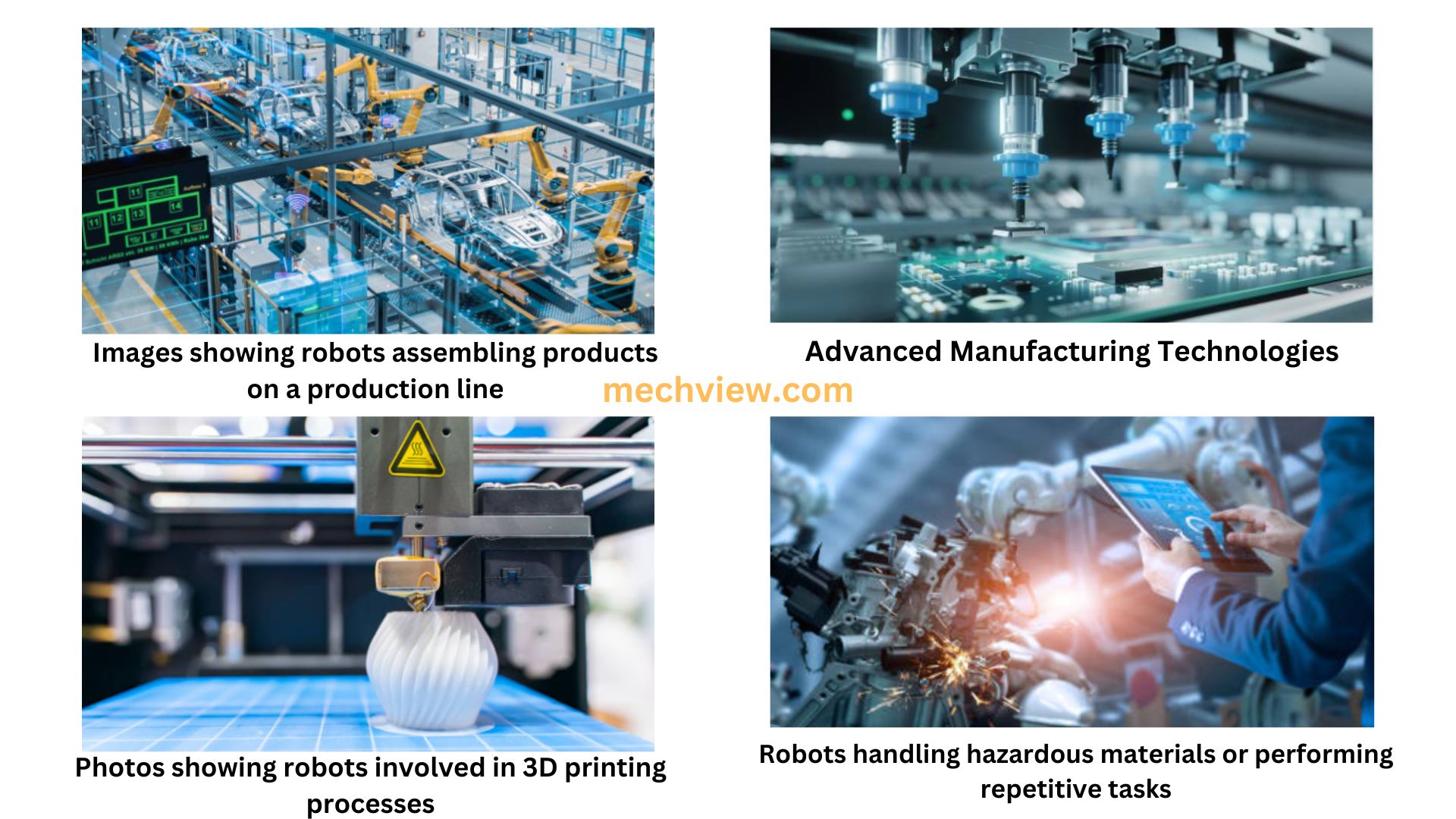
Benefits of Robotics and Automation
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automation significantly reduces production time and operational costs. Robots can operate 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring consistent output and minimizing downtime.
Enhanced Precision and Quality
Robots execute tasks with unparalleled accuracy, reducing human error and ensuring high-quality products. Automated systems also maintain uniformity and precision in manufacturing processes.
Improved Safety and Working Conditions
By taking over hazardous tasks, robots reduce workplace accidents and injuries. Automation also alleviates workers from repetitive and strenuous activities, improving overall job satisfaction.
Scalability and Flexibility
Automated systems can be scaled up or down based on production requirements. Flexible automation allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Challenges of Adopting Robotics and Automation
High Initial Investment
Implementing robotics and automation requires substantial upfront investment in equipment, software, and training. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may find it challenging to bear these costs.
Workforce Displacement
Automation can lead to job displacement, particularly for low-skilled workers. Companies must invest in reskilling and upskilling their workforce to ensure a smooth transition.
Complex Integration
Integrating advanced robotics and automation into existing manufacturing systems can be complex and time-consuming. It requires careful planning, testing, and coordination.
Cybersecurity Risks
Connected systems are vulnerable to cyber threats. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is critical to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has been a frontrunner in adopting robotics and automation. Companies like Tesla and Toyota leverage advanced robotics for assembly, painting, and welding, resulting in higher efficiency and precision.
Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics giants such as Apple and Samsung utilize automation for tasks like component placement and soldering. This ensures high-quality products and rapid production cycles.
Food and Beverage Industry
Automation in the food and beverage industry enhances production efficiency, consistency, and safety. Robots handle packaging, sorting, and palletizing, reducing contamination risks.
Future Trends in Robotics and Automation
AI-Powered Robotics
The integration of AI in robotics will continue to advance, enabling robots to learn from experiences, adapt to new tasks, and make autonomous decisions. This will further enhance their versatility and efficiency.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Cobots will become more prevalent, working alongside humans in various industries. Enhanced safety features and intuitive interfaces will make cobots easier to deploy and operate.
Advanced Sensor Technology
Developments in sensor technology will improve robots’ perception and interaction capabilities. This will enable more precise and adaptive manufacturing processes.
Additive Manufacturing and Robotics
Combining additive manufacturing (3D printing) with robotics will revolutionize production methods. Robots will handle complex 3D printing tasks, creating customized and intricate parts efficiently.
Final Thoughts
Robotics and automation are transforming modern manufacturing, offering numerous benefits such as increased efficiency, precision, and safety. However, the adoption of these technologies comes with challenges, including high initial costs and workforce displacement. By addressing these challenges and embracing the latest advancements, manufacturers can stay competitive in an ever-evolving industrial landscape. The future of manufacturing lies in the seamless integration of robotics and automation, driving innovation and growth across various sectors.
“MechView: Unveiling Mechanical Engineering, Simply Explained!”